Hey all! To develop our app further, we need to do two more vital things – configuration and logging. We will use the nconf module for configuring:
npm i nconf
It is definitely a weak idea to write port 3000 in the app and further specify connection to the database and so on. So, we put nconf and now can look at documentation. We can configure the module, which means we connect it and then tell to this module where it can read configuration. The line is:
nconf.argv()
.env()
.file({ file: 'path/to/config.json' });
Which means: read configuration from the command line, environment variables and files. Let us now create config directory, create index.js in it and connect nconf there. Next copy configuration from the documents into it changing it a little bit (the file will be from the current directory), specify the path:
var nconf = require('nconf');
var path = require('path');
nconf.argv()
.env()
.file({ file: path.join(__dirname, 'config.json') });
module.exports = nconf;
In the first config (create the file config inside our new directory – config.json) let us write: port: 3000.
{
"port": 3000
}
Attach the config module to app.js:
var config = require('config');
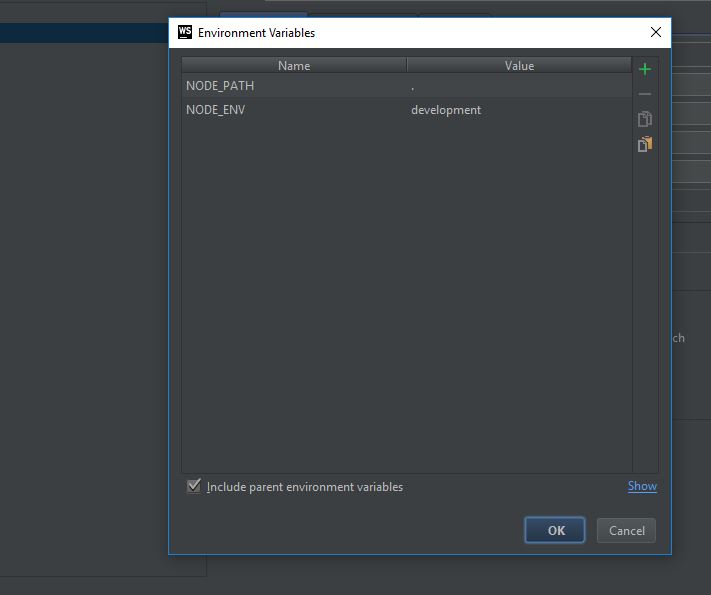
change the launch configuration a little bit for it to find this module and add NODE_PATH.
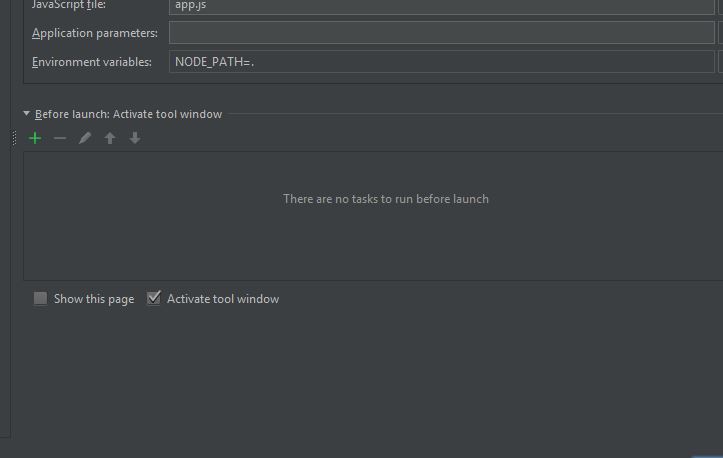
Also, within app.js add the method config.get:
app.set('port', config.get('port'));
http.createServer(app).listen(app.get('port'), function(){
console.log('Express server listening on port ' + config.get('port'));
});
Check it. Everything works!
The next thing we should do is to install a logger:
npm i winston
We will use our own wrap over winston. In order to find the right place for putting it, create the directory libs. Here we will put those modules and files that do not fall out anywhere, but we still some place for them. In our case, logging is the file log.js, (create it), which will be in this directory. Here is an example of such wrapping:
var winston = require('winston');
var ENV = process.env.NODE_ENV;
// can be much more flexible than that O_o
function getLogger(module) {
var path = module.filename.split('\\').slice(-2).join('\\');
return new winston.Logger({
transports: [
new winston.transports.Console({
colorize: true,
level: (ENV == 'development') ? 'debug' : 'error',
label: path
})
]
});
}
module.exports = getLogger;
We get the environment. In our file log.js we’ll get the environment directly from NODE_ENV. In order to make it work, let us add the launch configuration with NODE_ENV development.
What does this wrap do? If someone anchors a logger (let us add the record to app.js) , for example:
var log = require('libs/log')(module);
the function getLogger takes a module and generates a special logger object for it. It may have some transporting means activated or switched off, a correct logging level, and so on. The only difference is a mark. So, let us see what thing it is and how it will work.
Take the logger and do log.info instead of console.log:
http.createServer(app).listen(app.get('port'), function(){
log.info('Express server listening on port ' + config.get('port'));
});
Launch it. The logger outputs everything first in different colors, second – if there is development, it outputs the debug level and above, while remaining on production, if outputs error. In this case, we’ve got development, so everything is visible for us.
Moreover, the logger has a mark:
....\node_js_lessons\app.js]
which means what its original file was. Sometimes it is very interesting to know such things. So, we take module.filename and get 2 last elements of the path. Let’s move on now.
We will work on outputting a standard HTML page. We’ve got some Middlewares, but we will cut them and take the Middlewares built into Express. So, we need the settings:
// app.set('views', __dirname + '/views');
// app.set('view engine', 'ejs');
These are the settings for a templating system, while our template engine will be ejs. Let us change the name of our views directory to templates. You may have any other templating system in your case – in fact, there are many of them. We will get rid of the port because there is obviously no reason to add it inside the app:
// app.set('port', process.env.PORT || 3000);
app.set('port', config.get('port'));<br>
Let us do a normal config and take settings out of it. Moreover, we will add other Middlewares that we’ve got. Our app.js will look like:
var express = require('express');
var http = require('http');
var path = require('path');
var config = require('config');
var log = require('libs/log')(module);
var app = express();
app.set('views', __dirname + '/templates');
app.set('view engine', 'ejs');
app.use(express.favicon());
app.use(express.logger('dev'));
app.use(express.bodyParser());
app.use(express.methodOverride());
app.use(express.cookieParser('your secret here'));
app.use(express.session());
app.use(app.router);
app.use(express.static(path.join(__dirname, 'public')));
app.use(function(err, req, res, next) {
// NODE_ENV = 'production'
if (app.get('env') == 'development') {
var errorHandler = express.errorHandler();
errorHandler(err, req, res, next);
} else {
res.send(500);
}
});
// var routes = require('./routes');
// var user = require('./routes/user');
// // all environments
// app.get('/', routes.index);
// app.get('/users', user.list);
http.createServer(app).listen(config.get('port'), function(){
log.info('Express server listening on port ' + config.get('port'));
});
Please stay tuned, we’ll continue in th nx article!
The lesson code can be found here.
The materials for this article have been borrowed from the following screencast.
We are looking forward to meeting you on our website soshace.com