AsyncStorage is the persistent storage in React native that is based on key-value pair storage. It is commonly used when we want to store some basic data like app settings. All values in AsyncStorage are stored as plain text since it does not support any other data type. In this post, we will learn the basics of using AsyncStorage in a React native app.
Set up on Android and iOS
We can add the async-storage package to our project using yarn.
$ yarn add @react-native-community/async-storage
Async-storage comes with the auto-linking feature for React native 0.60+.
For iOS using cocoapods, run:
$ cd ios/ && pod install
We can now import the package to our project.
import AsyncStorage from '@react-native-community/async-storage';
Commonly Used Methods
Here, we will discuss the four commonly used methods in AsyncStorage that follow the get and set principle.
Store Data
storeData = async () => {
try {
await AsyncStorage.setItem('random_time', 50000)
} catch (e) {
// saving error
}
}
Get Data
getData = async () => {
try {
const value = await AsyncStorage.getItem('random_time')
if(value !== null) {
// value previously stored
}
} catch(e) {
// error reading value
}
}
Delete Individual Key
removeValue = async () => {
try {
await AsyncStorage.removeItem('random_time')
} catch(e) {
// remove error
}
console.log('Done.')
}
Clear All Data
clearAll = async () => {
try {
await AsyncStorage.clear()
} catch(e) {
// clear error
}
console.log('Done.')
}
First Basic Example: When I Die App
Our app follows a simple idea. It uses some random time value that is set as a react-native-countdown-component. After the countdown is started, the current time will be stored in AsyncStorage when we close the app and the componentWillUnmount event fires. When we open the app again and componentDidMount event fires, the app will retrieve the counting down time value from AsyncStorage and continue.
Initialize New Project
Using the VsCode integrated terminal, we can create a new react-native project using the following command.
react-native init asyncstorage_demo
To open the project, run:
code asyncstorage_demo
Now we need to add the two required packages, async-storage and react-native-countdown-component, using yarn.
yarn add react-native-countdown-component @react-native-community/async-storage
Bootstrap the App
Import the installed packages to our project file, App.js.
import CountDown from 'react-native-countdown-component';
import AsyncStorage from '@react-native-community/async-storage';
Define a new state for the component.
export default class App extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {until_death: 10000}
}
...............
Render our component to show the countdown clock.
return (
<View style={styles.MainContainer}>
<Image source={require('./img/grave.png')} />
<Text style={styles.header}>Your will die in</Text>
<CountDown
until={this.state.until_death}
onFinish={this.onDoneCountdown}
onPress={this.onPressCountdown}
size={40}
digitStyle={{backgroundColor: 'black'}}
digitTxtStyle={{color: 'red'}}
onChange={until_death => this.setState({until_death: until_death})}
/>
</View>
);
}
If we closely inspect the code inside the render function, first we set the initial time.
until={this.state.until_death}
When the time changes, we set the state of until_death to the new value.
onChange={until_death => this.setState({until_death: until_death})}
Next, we should store the state when the user closes the app so that when the user opens the app again the countdown continues.
storeData = async until_death => {
try {
await AsyncStorage.setItem('until_death', until_death);
} catch (e) {
console.log(e);
}
};
The componentWillUnmount event fires when the user closes the app. We will call the storeData function when this event fires and sends the current state as a parameter.
componentWillUnmount() {
this.storeData(this.state.until_death);
}
Continue Count Down
When the user opens the app again, getData function will retrieve the stored time. If the app is opened for the first time, it will initialize a random value for until_death and set the state of the app.
getData = async () => {
try {
const until_death = await AsyncStorage.getItem('until_death');
if (until_death !== null) {
this.setState(until_death);
} else {
let until_death = Math.floor(Math.random() * 1000000) + 1;
this.setState(until_death);
}
} catch (e) {
console.log(e);
}
};
When the user opens the app and the componentDidMount event fires, call the getData method to continue the countdown.
componentDidMount() {
SplashScreen.hide();
this.getData();
}
Our final app now continues the countdown from where it left off.
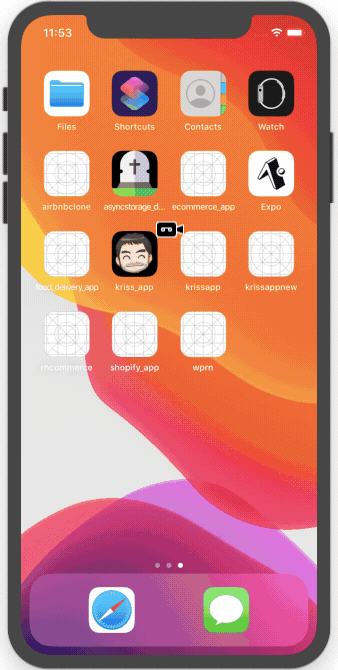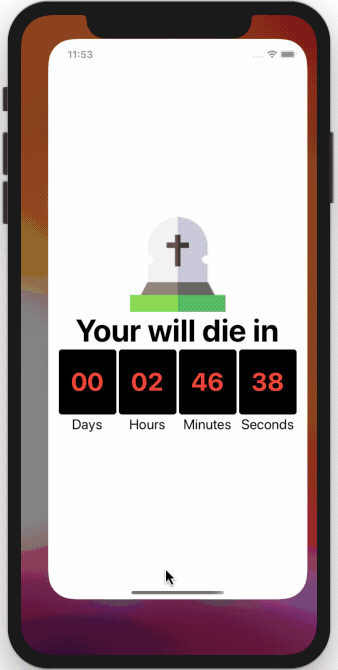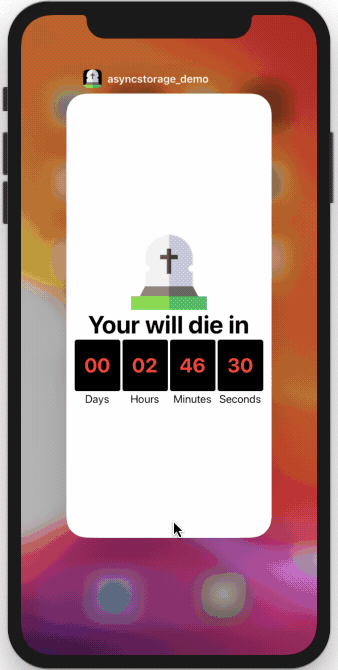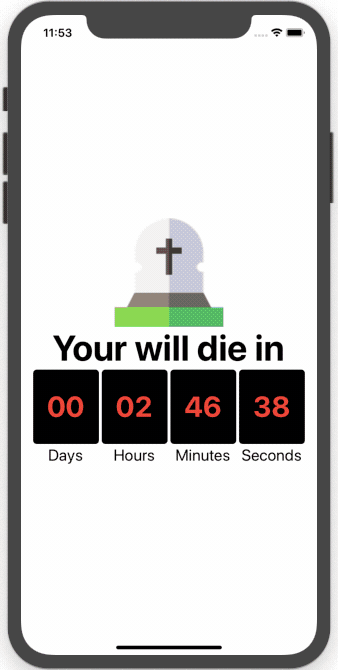
Conclusion
This post demonstrated the basics of using AsyncStorage in our app. Our current app does not continue the countdown in the background when the app closes. If you want to find out how to add this feature to our app, you can find the full source code here.
Credit
Icon made by Freepik from www.flaticon.com