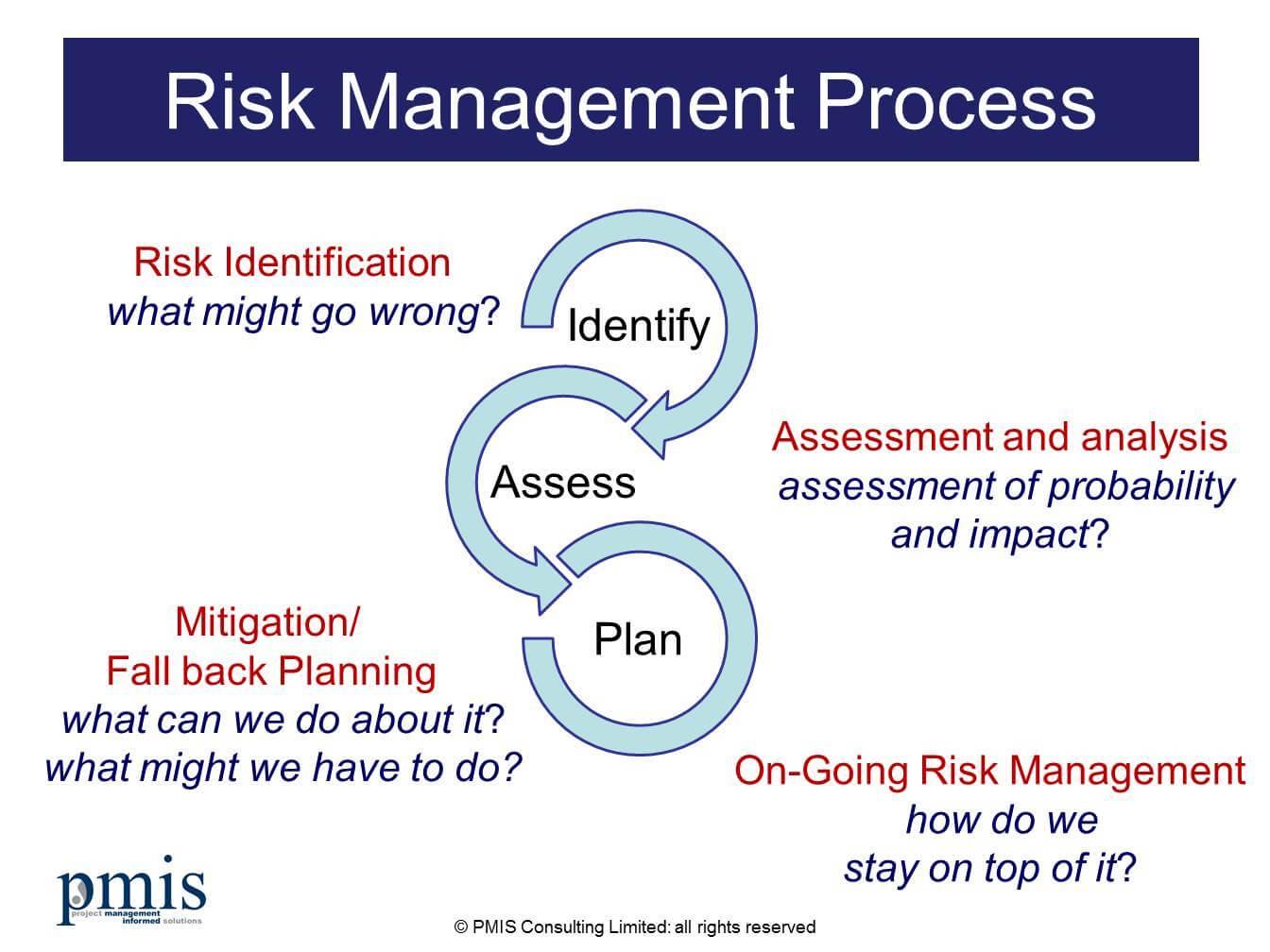
In today’s fast-paced and dynamic business environment, the ability to effectively manage project risks is crucial to the success of any organization. As projects become increasingly complex and interdependent, unforeseen challenges can threaten timelines, budgets, and ultimately, project outcomes. Navigating these risks requires a strategic approach that not only identifies potential pitfalls but also implements proactive measures to mitigate their impact. This article will explore effective strategies for managing project risks successfully, providing insights into best practices, tools, and frameworks that project managers can adopt to enhance their risk management processes. By fostering a culture of risk awareness and resilience, organizations can safeguard their projects and drive sustainable growth in an uncertain landscape.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Landscape of Project Risks
- Developing a Proactive Risk Management Framework
- Implementing Continuous Monitoring and Adjustment Practices
- Fostering a Risk-Aware Culture for Long-Term Success
- Insights and Conclusions
Understanding the Landscape of Project Risks
Project risks can arise from various sources and can significantly impact the success of any project. Recognizing the diverse nature of these risks is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies. Some common sources of project risks include:
- Technical risks: Issues arising from the technology being used, including compatibility and performance concerns.
- Financial risks: Budget overruns and unexpected costs that may affect the project’s financial viability.
- Operational risks: Failures in the processes or systems, often due to inadequate planning or resource allocation.
- External risks: Factors outside the organization’s control, such as regulatory changes, market fluctuations, or natural disasters.
To navigate this complex landscape effectively, project managers must employ comprehensive risk assessment techniques. Utilizing tools such as SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) and building a robust risk register can provide valuable insights into potential downturns. A well-structured risk management framework often includes:
| Risk Category | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|
| Technical | Conduct thorough testing and invest in quality assurance. |
| Financial | Establish a contingency budget and monitor expenses closely. |
| Operational | Regularly review processes and provide adequate training. |
| External | Create flexible plans to adapt to evolving external conditions. |
Developing a Proactive Risk Management Framework
In today’s constantly evolving business landscape, establishing a robust framework for risk management is essential for identifying, evaluating, and mitigating potential project challenges. A proactive approach should encompass a variety of elements, including thorough risk assessments, stakeholder engagement, and the implementation of effective monitoring techniques. By critically analyzing potential risks at the outset, teams can formulate strategies that not only address immediate concerns but also anticipate future obstacles.
Key components of this framework should include:
- Risk Identification: Utilize tools like brainstorming sessions and SWOT analysis to pinpoint potential risks.
- Risk Analysis: Assess the likelihood and impact of identified risks through qualitative and quantitative methods.
- Response Planning: Develop actionable strategies to mitigate, transfer, or accept risks based on their severity.
- Monitoring and Review: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to track risk factors continuously and adapt strategies as necessary.
| Risk Category | Risk Level | Proactive Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Financial | High | Allocate budget reserves |
| Technical | Medium | Conduct regular software updates |
| Operational | Low | Streamline processes through training |
Implementing Continuous Monitoring and Adjustment Practices
To effectively navigate the fluctuating landscape of project management, establishing a framework for ongoing monitoring and adjustment is crucial. This approach allows project managers to remain agile and responsive to emerging risks. Key practices to incorporate include:
- Regular Risk Assessments: Conduct frequent evaluations of potential risks, allowing for timely identification and mitigation strategies.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Foster open communication channels with all project stakeholders to gather diverse insights and feedback.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Utilize analytics and performance metrics to shape project strategies and adapt to potential threats.
- Iterative Review Cycles: Implement a structured review timetable that aligns with project milestones to reassess and refine risk management approaches.
Successful adjustment practices hinge on not only recognizing existing risks but also predicting possible future challenges. By leveraging technology and collaborative tools, teams can ensure that adjustments are implemented seamlessly. An example framework for adjustment includes:
| Adjustment Type | Frequency | Responsible Parties |
|---|---|---|
| Scheduled Reviews | Monthly | Project Manager, Stakeholders |
| Ad-hoc Assessments | As Needed | Team Leads |
| Risk Training | Quarterly | HR, Project Team |
Fostering a Risk-Aware Culture for Long-Term Success
Building a risk-aware culture within an organization is essential for achieving long-term success in project management. This culture encourages team members to proactively identify and communicate potential risks, fostering an environment where issues can be addressed before they escalate. Key elements of a risk-aware culture include:
- Open Communication: Encourage transparent discussions about risks among all team members.
- Training and Development: Provide regular training to enhance risk assessment skills.
- Empowerment: Allow team members to take ownership of their roles in risk management.
Moreover, integrating risk management into the decision-making process ensures that every project aligns with the organization’s strategic objectives. Establishing a consistent framework for assessing risks not only standardizes the approach but also helps team members feel secure in their roles. Consider implementing a simple risk assessment matrix as a visual tool:
| Risk Level | Likelihood | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Low | Unlikely | Minimal |
| Medium | Possible | Moderate |
| High | Likely | Severe |
This matrix aids teams in prioritizing risks, ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently to mitigate the most critical concerns. Ultimately, by cultivating a risk-aware culture, organizations not only enhance their resilience but also prepare themselves to navigate complexities and achieve enduring success in project management.
Insights and Conclusions
effective project risk management is not merely a reactive process but a proactive strategy integral to the success of any project. By identifying potential risks early, assessing their impact, and implementing robust mitigation strategies, organizations can safeguard their projects against unforeseen challenges. Each strategy discussed—from thorough risk assessments and continuous monitoring to fostering a risk-aware culture—plays a crucial role in enhancing project resilience. As the business landscape continues to evolve, adopting these strategies will not only help mitigate risks but also empower teams to navigate uncertainties with confidence. Investing in risk management is investing in the sustainable success of your projects and, ultimately, your organization’s future. Embrace these strategies, and ensure that your project management practices are equipped to turn potential threats into opportunities for growth and innovation.